Indian herbal formulation Kaba Sura Kudineer possesses the most powerful ligands to block ACE2-RBD interaction of SARS-CoV-2 infection
Abstract
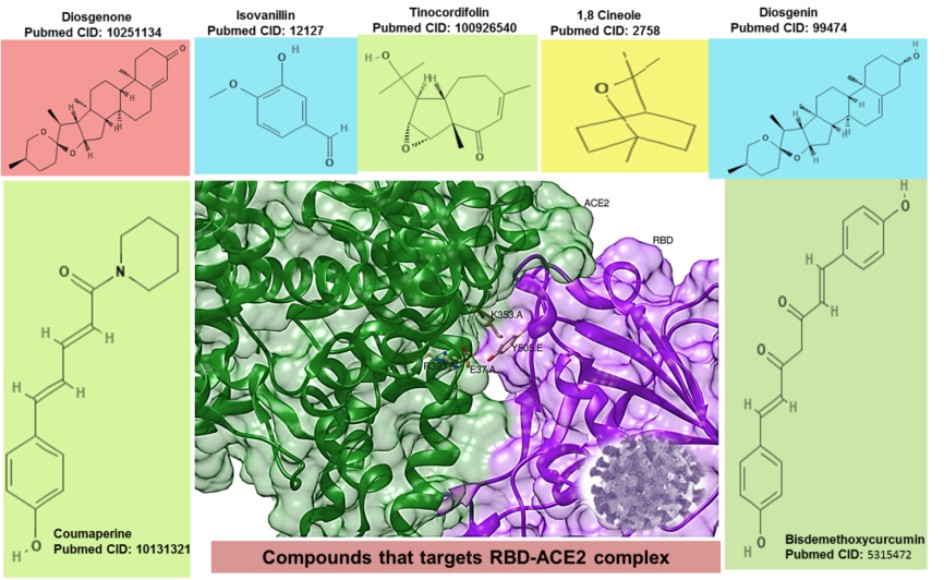
Medicinal herbs play an important role in the primary health care system of developing countries and always uphold the importance of ethnomedicinal studies in the drug discovery process. Indian Siddha practitioners urged people to consume a polyherbal formulation named ‘Kaba Sura kudineer (KSK)’ as a prophylactic measure against COVID-19. To validate the presence of anti-COVID 19 agents if any in KSK, virtual screening of 80 phytochemicals was done by blind docking, fixing the RBD-ACE2 complex as the target using PyRx software. The binding energy of the compounds was calculated using Autodock Vina. The SWISSADME server was used to identify the phytochemicals that obey the Lipinski rule and the blood-brain barrier permeability of the compounds. The outcome of the study revealed that phytochemicals such as diosgenin, diosgenone, coumaperine, bisdemethoxycurcumin, tinocordifolin, isovanillinand 1,8-Cineole displayed hydrogen bond interactions with the complex residues in the interacting site (−8.9 to −5.1 kcal/mol) and were found to obey the Lipinski rule as well as possess blood-brain barrier (BBB) permeability. Based on the highest docking score and the more number of interacting residues at the active site herein we suggest diosgenin and bisdemethoxycurcumin as potential inhibitors of SARS-Co-V-2.
Keyword(s)
COVID-19; Herbal medicine; Kaba sura kudineer; Molecular docking; Phytochemicals
Full Text: PDF (downloaded 1204 times)
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.